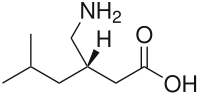
Pregabalin API
| Cas No : | 148553-50-8 |
|---|---|
| Name : | Pregabalin |
| Synonyms : | (3S)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid |
| Molecular Formula : | C8H17NO2 |
| Melting Point : | 194-196°C |
| Boiling Point : | 274 °C |
| Molecular Weight : | 159.23 g/mol |
| Density : | 0.997±0.06 g/cm3 |
| Solubility : | Freely soluble in water and both basic and acidic solutions |
Uses :
- Pregabalin is used to treat epilepsy and anxiety. It's also taken to treat nerve pain. Nerve pain can be caused by different conditions including diabetes and shingles, or an injury. Pregabalin works in different ways: in epilepsy it stops seizures by reducing the abnormal electrical activity in the brain with nerve pain it blocks pain by affecting the pain messages travelling through the brain and down the spine in anxiety it stops your brain from releasing the chemicals that make you feel anxious